-
- Shop
- Shop By Brand
- Shop By Health Need
Item added to your cart

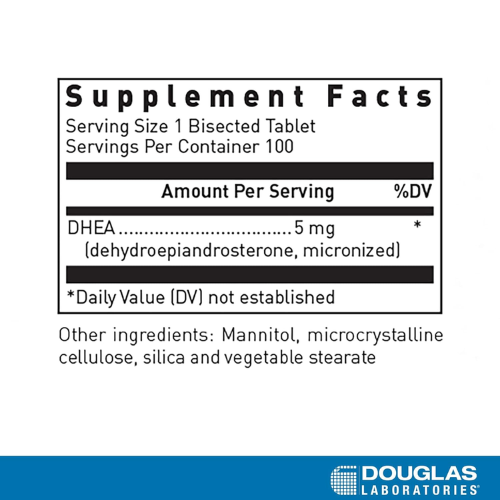
DHEA is a natural steroid hormone that is synthesized from cholesterol through pregnenelone by the adrenal glands. DHEA acts as an antagonist for glucocorticosteroid hormones and is the parent precursor for other important steroid hormones, such as estradiol and other estrogens, and testosterone. While not a precursor to progesterone, DHEA can indirectly influence progesterone synthesis through a feedback mechanism whereby pregnenelone is converted to progesterone based on DHEA levels. Apart from these functions, DHEA also has important biological functions itself. Recent experimental and human studies show that DHEA is involved in a large variety of physiological processes, including immune function, brain function, bone metabolism, blood lipid metabolism, energy metabolism, the regulation of normal blood sugar and insulin levels, and the maintenance of lean body mass.